6
EDUCATION
1
Work with a partner and answer these questions.
1
What can you remember about Maria Montessori?
2
What is the Montessori method?
2
a
6
You are going to watch an interview with
Rob Gueterbock, who works at a Montessori school.
Watch the interview and complete sentences 1 and 2
with phrases a–h. Which phrase can go in both
sentences?
1
In traditional education, children …
2
In Montessori education, children …
a
are able to follow their own interests.
b
learn by doing, not by listening.
c
learn according to a curriculum.
d
learn with the whole class.
e
learn individually and in small groups.
f
form mixed age communities.
g
learn only with children of the same age.
h
learn at their own pace.
2
b
Watch the interview again and take notes on the
following.
1
Reasons for becoming a Montessori teacher
2
The Montessori method of learning
3
Why Montessori schools call teachers ‘guides’
4
Montessori education in different countries
5
What Rob thinks about children and technology
2
c
Compare your notes with a partner.
3
a
Imagine that you have been asked to give a report
to the Ministry of Education in another country. The
Ministry wants to improve the level of education of
school children aged 6–16. Work in three groups. Each
group should give a short report on the advantages of
three different approaches to education. Decide
on a definition for your group’s approach to education.
Then decide on the advantages of your group’s
approach to education.
•
Group A: traditional education
•
Group B: Montessori education
•
Group C: digital education
3
b
Take turns to give your reports. Decide which
group gave the best reasons.
7
DESIGN
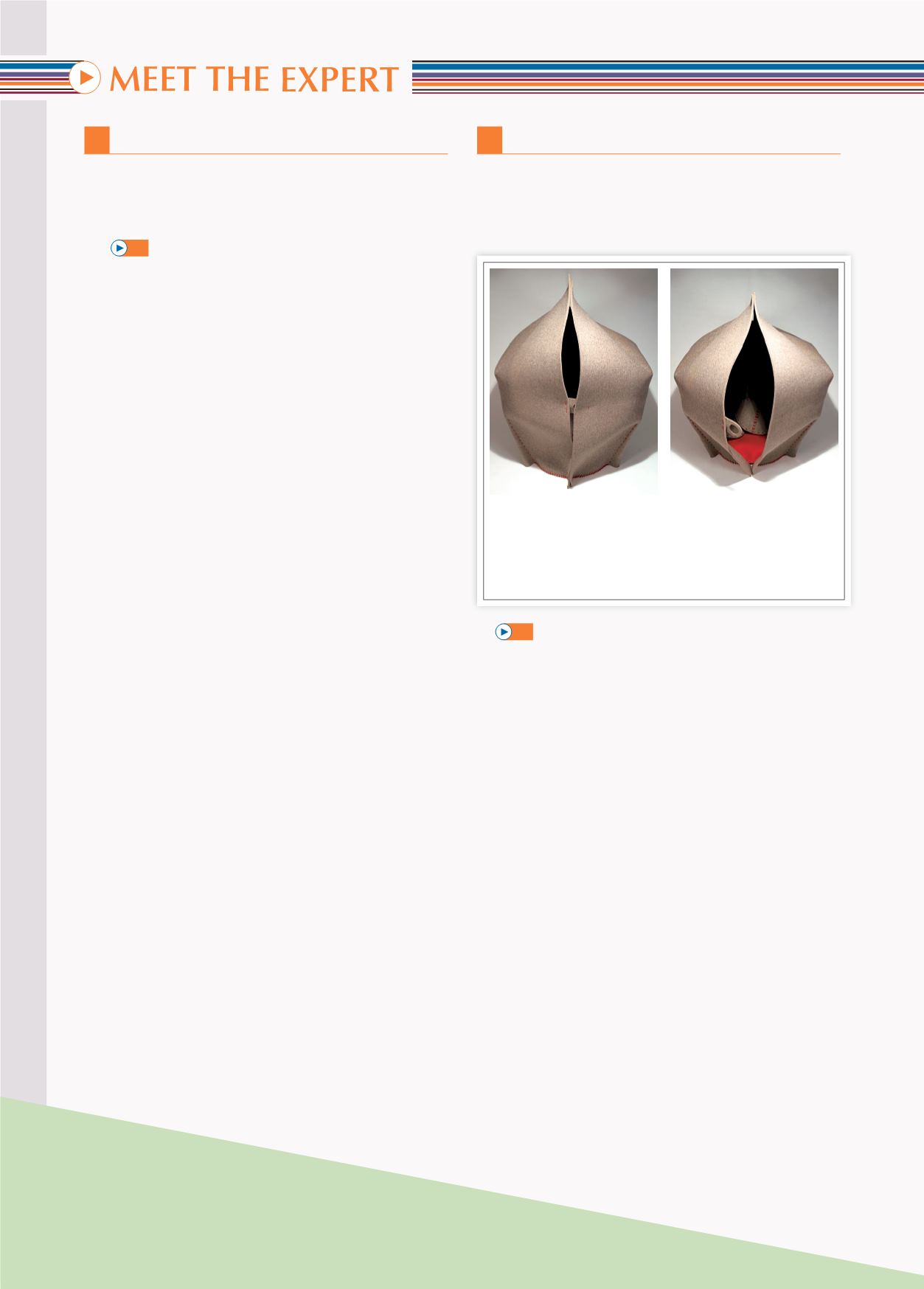
1
Work in groups of three. Look at the photos of the
‘hush pod chair’ by product and furniture designer
Freyja Sewell, then discuss the five questions in the
extract below from a book about design.
2
7
Watch the interview with Freyja. Tick (
ü
) the
adjectives you hear.
•
sustainable
•
elegant
•
innovative
•
natural
•
mass-produced
3
a
Watch the interview again. Match each object or
material (1–6) to its description in the video (a–f).
1
a light bulb
2
a chair
3
wool felt
a
something connected to a particular country
b
something used because it was hard
c
something used because it was soft
d
something used because it was natural
e
something developed in another country
f
something that is an example of a good design
3
b
How do we know that materials are important to
Freyja?
4
Do you own a mobile phone, smart phone or tablet
computer? Work in groups. Compare the designs of your
phones or tablet computers by discussing these features.
•
form (style and beauty)
•
sound design (e.g. does it ‘click’ or ‘whistle’?)
•
function and efficiency
4
wool
5
starch
6
starch-bound wool
•
renewable
•
careful
•
traditional
•
rigid
•
disposable
Designers have to ask themselves questions such as:
‘Is the product really wanted?’,
‘How is it different from everything else on the market?’,
‘Does it fulfil a need?’,
‘Will it cost too much to manufacture?’
and ‘Is it safe?’.
152


